Comparison of air humidification types
- Air washer (circulating spray humidifier) - indirect humidification
- Steam humidifier (Electrical: Electrode - Resistance) - indirect or direct humidification
- Steam humidifier (gas fired) - indirect humidification
- Ultrasonic humidifier - indirect or direct humidification
- Cold evaporation systems - indirect or direct humidification
- Two-component low-pressure air humidification (compressed air) - indirect or direct humidification
- One-component low-pressure air humidification - indirect or direct humidification
- One-component high-pressure air humidification - indirect or direct humidification
Energy use and properties of humidification
Circulating spray humidifiers
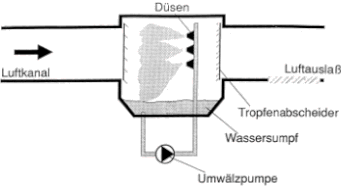
Circulating spray humidifiers (air washers) are indirect humidifying solutions and humidify by roughly spraying against a droplet separator. Most of the water that has not evaporated is
circulated.
To the detriment of hygiene: chemical additives, high blow-down rates, complex disinfection and very large and regular maintenance costs are the result. The circulating pump of the circulating
spray humidifier requires a comparatively high amount of electrical energy for the permanent supply of the nozzles.
The use of water for regular fresh water (temporary water exchange) to avoid premature infections is considerable. Droplet separators are required for operation.
Steam humidifier (Gas/Electric)
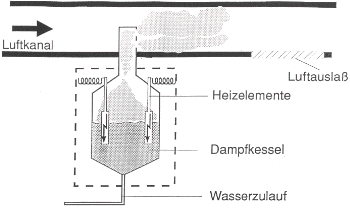
Properly configured and designed, steam humidifiers humidify extremely hygienically through the evaporation of water.
Air humidification with water vapor in which the air temperature remains essentially constant during humidification is called isothermal air humidification. Since the steam is generated under
atmospheric pressure, the room temperature remains almost unchanged.
However, they require a large amount of energy in the form of fossil fuels or electrical energy. This puts a considerable strain on the energy and pollutant balance of certified companies. The
wear and tear of heating electrodes, heating spindles or the inspection of the gas firing system are reflected in the operating costs, as is the maintenance and cleaning of the steam pressure
tank or steam boiler.
In addition, a steam humidifier can also be hygienically questionable. When gram-negative bacteria die, endotoxins can be released through cell division. These are not destroyed by cooking and
can cause inflammation.
Ultrasonic Humidifier
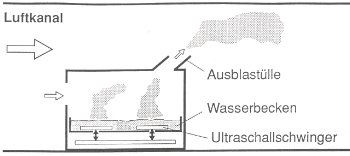
Ultrasonic humidifiers require a water basin to generate mist droplets (aerosols).
These humidifier units are open and are supplied with hyper-filtered osmosis water. In addition, the hygiene flushing cycles of the water basin are taken into account in the controls.
Nevertheless, they remain open systems in which contamination cannot be ruled out.
In addition, the energetic balance in relation to the humidification performance is rather negative, e.g. B. compared to high-pressure systems. In addition, the service life of the ultrasonic
vibrators is limited (approx. 1 year) and must be replaced.
Cold evaporator

Cold evaporators are glass fiber cellulose, ceramic or stainless steel honeycombs over which the quantity-controlled water is guided and e.g. installed in the air flow of ventilation
systems.
They can also be installed as mobile versions with integrated and controlled air fans.
In these systems, the control is sluggish and not very precise. Depending on the system, a lot of return water can occur.
Depending on the system, water quality and system control, attention must also be paid to hygiene safety. Furthermore, pressure losses can occur due to the evaporator elements, which also
increases the electrical power consumption of fan motors.
Two-substance humidifier (compressed air)
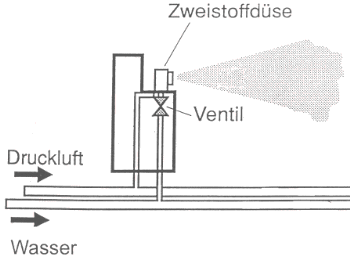
Two-substance humidification systems can be operated indirectly (duct) or directly (room). They are usually supplied with cleaned compressed air and deionized water. The closed structure of the
systems ensures hygienic operation. Droplet separators are required for indirect use in a duct.
The relatively high consumption of compressed air is rather expensive in terms of energy and the noise emitted by the nozzle air discharge can spread through the duct and become a disruptive
factor.
Single-substance humidifier (high pressure / low pressure)

Single-component humidification systems using high-pressure or low-pressure pumps can be operated indirectly (channel) or directly (room). In the majority of cases, humidification takes place via
a regulated pump which is supplied with fully demineralised water.
The closed structure of the systems ensures hygienic operation. Separators or droplet separators are required for indirect use in a channel.
Depending on the system, low-pressure or high-pressure nozzles or, in the case of the high-pressure system, ventilation-supported atomizers are used for direct use.
The relatively low energy consumption of these systems is very interesting in terms of energy compared to the possible humidification capacity (min/max.).


